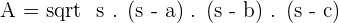Trigonometry doesn't only end on trigonometric ratios, it has a lot of purpose in our lives. It has many applications such as in engineering, telecommunication, physics, astronomy, and many more. This lesson covers trigonometric laws. Whenever we talk about trigonometric laws, we usually think about two specific laws and they are:
- Sine Law
- Cosine Law
However, these are not the only laws available, there are other laws as well that deserve the same amount of respect.

Sine Law
With the help of the sine law, you can find an angle or length of a side of a triangle. Do note that this law is only applicable to triangles only so if you are working on another geometry that is not a triangle or can't be transformed into a triangle then this law will not be valid. Each side of a triangle is directly proportional to the sine of the opposite angle. In easy words, the ratio of the side and the  of the opposite angle is equal to another ratio of another side and
of the opposite angle is equal to another ratio of another side and  of the opposite angle. This might be a little hard to understand hence, let's imagine a triangle.
of the opposite angle. This might be a little hard to understand hence, let's imagine a triangle.
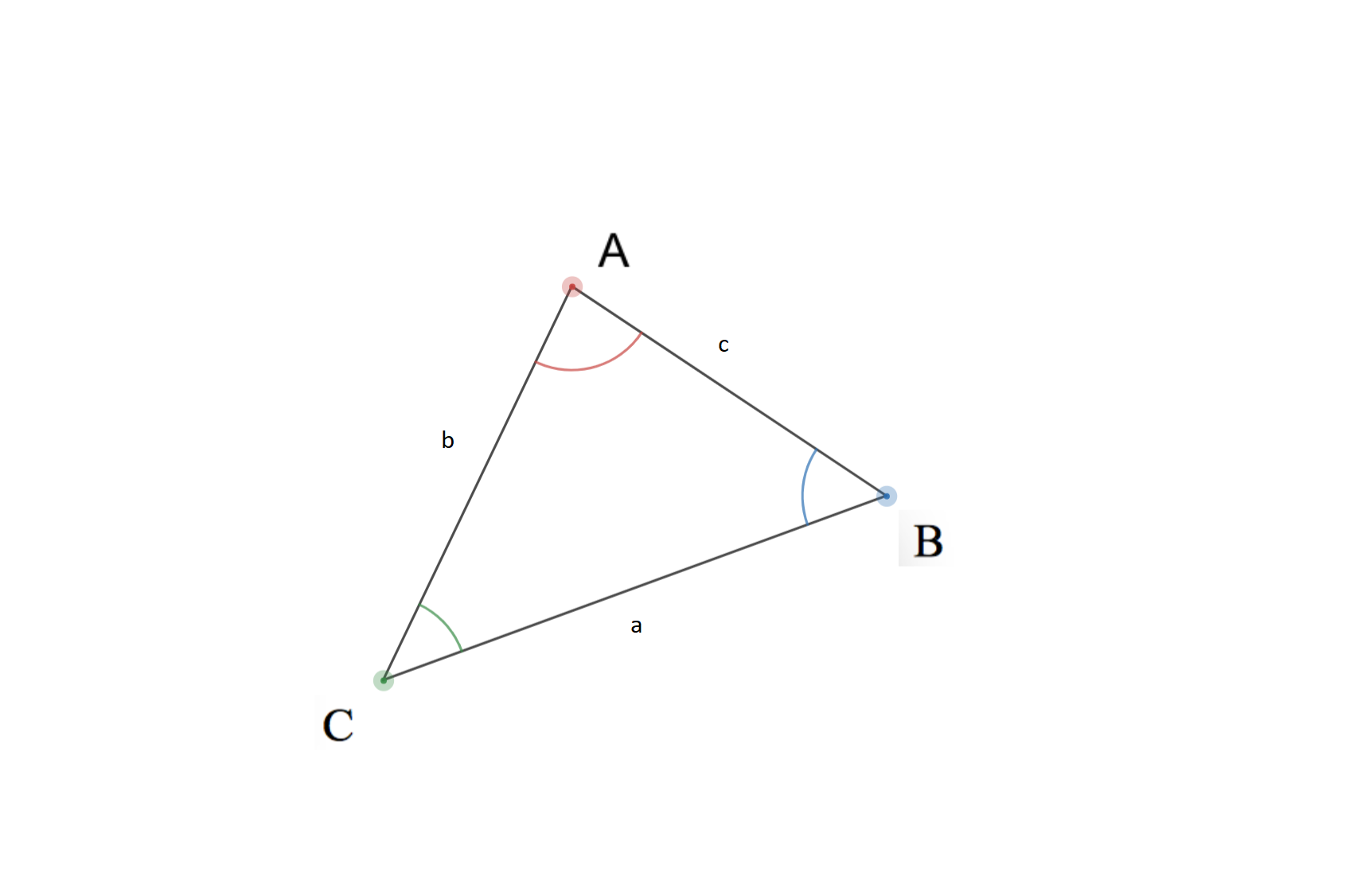
The triangle has three sides which are "a", "b", and "c". Now focus on the side "a" and then look at the opposite corner of the triangle and mark it "A". That "A" is the angle A. Repeat this process and mark angle B and angle C. Now apply the sine law. The ratio of side a and sine of angle A is equal to the ratio of side b and sine of angle B and also equal to the ratio of side c and angle C.

Example
Find the sides BC and AC of the triangle given below.
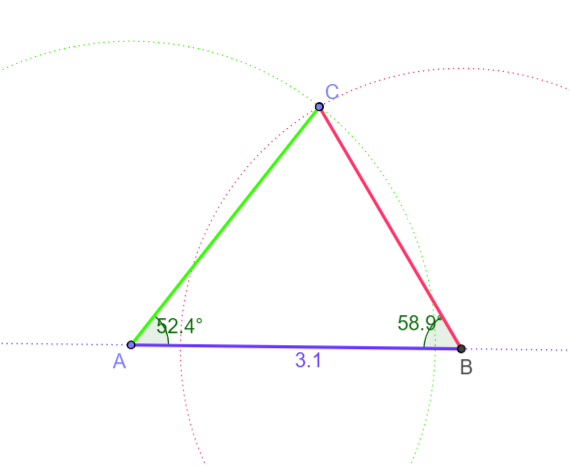


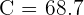
FOR BC:

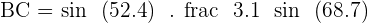

FOR AC:

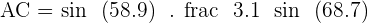
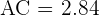
Cosine Law
Although, sine law can be applied on SAS (Side-Angle-Side) as well as ASA (Angle- Side- Angle) triangles but cosine law can only be applied to SAS (Side-Angle-Side) triangles. In a triangle, the square of every side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two less the double product of the product of both for the cosine of the angle that they form.


This formula can be altered in many ways. For example, you want to find the length b then the formula will be as follows:
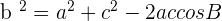

In case, if you want to find the angle and you are given two sides then:

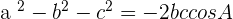


The above formula is in terms of angle A, you can alter it to find other angles (i.e. angle B and angle C):

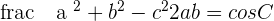
Other Trigonometric Laws (Related to Triangles)
Derivative of Sin Law

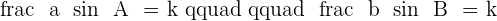
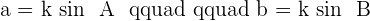


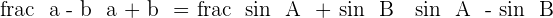
________________________________________________________________
Following trigonometric identities are applied:


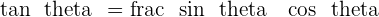
_________________________________________________________________




Final Answer: 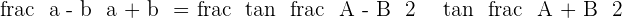
However, in some text books, you might find like this: 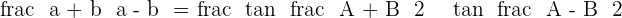 , there is no need to panic, just inverse both sides of the above answer and you will get this form:
, there is no need to panic, just inverse both sides of the above answer and you will get this form:
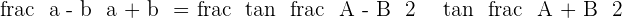
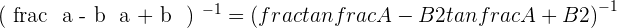
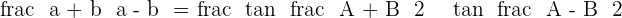
Area of Triangle with the help of Sine Law
The area of a triangle is half the product of the base and the height.
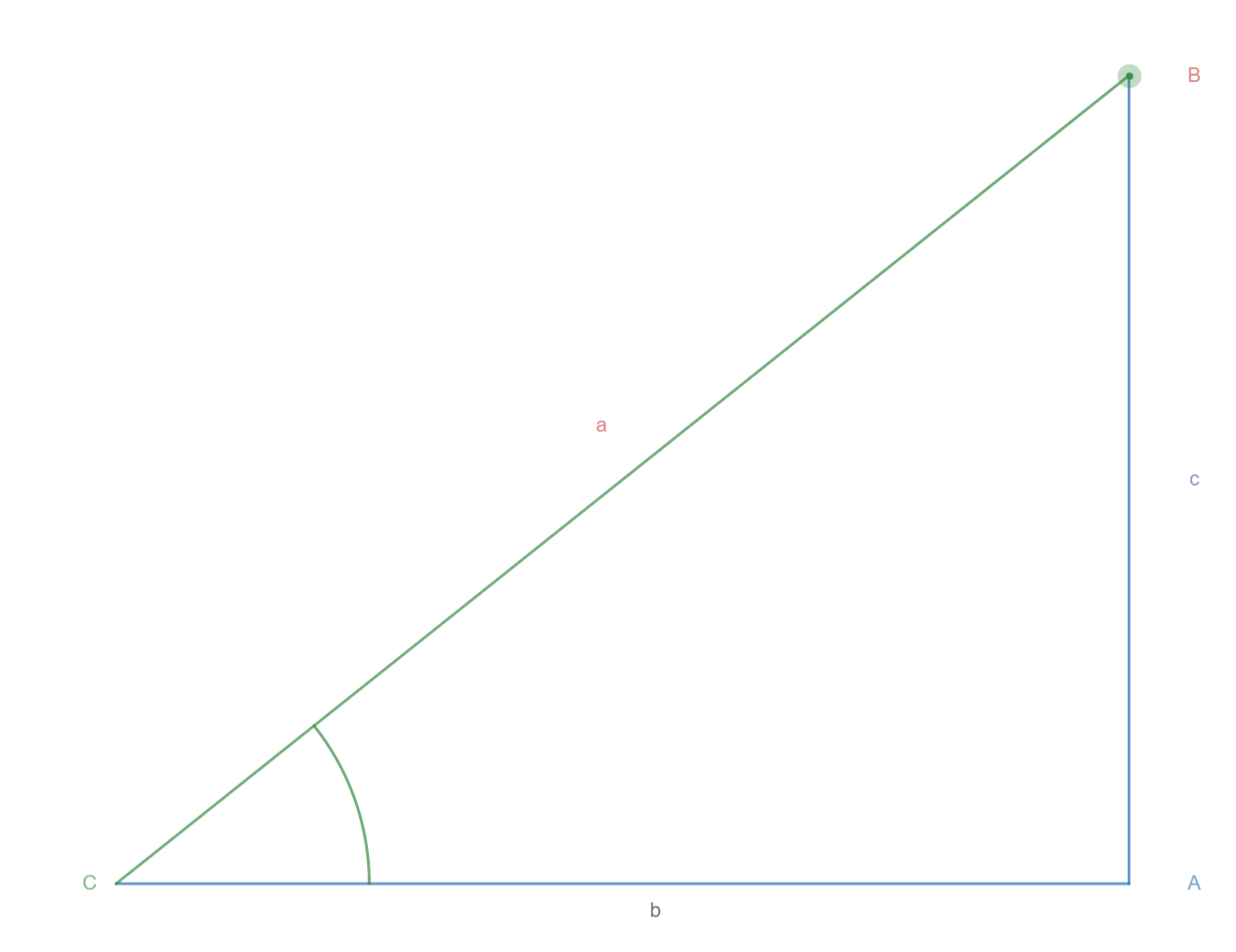

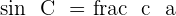


The area of a triangle is half the product of two sides by the sine of the angle that they form.
The area of a triangle is the quotient between the product of its sides and four times the radius of its circumscribed circle.

The area of a triangle is equal to the product of the radius of the inscribed circle by the semi perimeter.

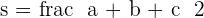
Heron's formula: