Chapters
In this article, we will discuss and compare the structure of a plant with the animal cell as observed under a light microscope. We will specifically discuss and compare the components of the plant cell such as the cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, vacuoles, and location of the cell membrane.

Introduction
Living organisms are made of cells. There are two types of living organisms: unicellular and multicellular. Unicellular organisms are made up of a single cell only, whereas multicellular organisms are made up of more than one cell. Cells of the living organisms can be observed under light and electron microscope. These microscopes magnify the images of these cells so that they can be studied in detail.
In the next section, we will discuss the structure of plant cells in detail.
Plant Cell
Plants are eukaryotic organisms that can manufacture their own food. Plants have chlorophyll which imparts green color and helps them to convert water and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and sugar by using sunlight. Any cell of the plant is known as the plant cell. Plants are made up of several cells which are the primary structural and functional units of plants. It is believed that plants were evolved from the green algae that were first found in the early Paleozoic era. An English natural philosopher, Robert Hooke, first observed the plant cells under a microscope. He observed microscopic pores in the plant cells that looked like a honeycomb. He coined the term cells for these microscopic pores. First, he thought that these cells are empty, however, with the invention of more advanced microscopes, the scientists were successful in observing the living components of the plant cells.
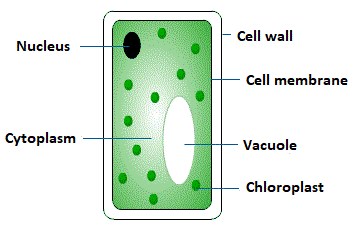
Structure of Plant Cells
Generally, a simple plant cell contains membrane-bound cell structures known as organelles that are suspended in the cytoplasm. A typical plant cell structure entails organelles, cytosol, cell membrane, and cell wall. The organelles of plant cells include the nucleus, plastids, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum. In this section, we will only discuss the major components such as cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and vacuoles.
Cell Wall
A rigid wall that surrounds the plasma membrane in the plant cell is known as a cell wall. It has a very complex structure and performs multiple functions. It not only protects the cell but also regulates the life cycle of the organism.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the highly specialized organelle of the plant cell that processes the information and acts as an administrative centre of the cell. The two primary functions of the nucleus are:
- to store the hereditary material, or DNA
- to coordinate the activities of the cell such as intermediary metabolism, growth, protein synthesis, and reproduction or cell division
Cytoplasm
Each plant cell is filled with a thick solution known as a cytoplasm which is also enclosed by the cell membrane. It is primarily made up of water, salts, and proteins. In eukaryotic organisms such as plants, the cytoplasm includes all the material present inside the cell and outside the nucleus. The organelles in the eukaryotic cells like the endoplasmic reticulum, nucleus, and mitochondria are present in the cytoplasm. The only part of the cytoplasm that is not contained in the organelles is known as the cytosol. It may seem that a cytoplasm has no structure or form, however, in reality, it is a highly organized structure.
Chloroplasts
One of the primary features of plants is that they can make their own food through a process known as photosynthesis. They do so by converting light energy into chemical energy. The process of photosynthesis is carried out in specialized organelles referred to as chloroplasts.
Vacuole
Each plant cell contains a large, single vacuole that performs multiple functions such as stores compounds, assists in plant growth and plays a vital structural role for the plant.
The following diagram shows the typical structure of a plant cell.
Structure of Animal Cells
Millions of cells make up an animal. Animal cells are characterized by their irregular structure and entail the following four key components:
- Cell membrane – An animal cell is surrounded by a flexible layer known as a cell membrane. This layer surrounds the cell and regulates the substances the enter or exit the cell.
- Nucleus – The nucleus in an animal cell contains genetic material (DNA), and controls the cell's activity.
- Cytoplasm – It refers to a jelly-like substance in an animal cell where the chemical reactions occur.
- Mitochondria – It is the part of the cell where energy is released from the food molecules.
All the above four components of an animal cell are shown in the diagram below.

In the next section of the article, we will compare the plant cell with an animal cell.
Plant Cell Vs Animal Cell
Plant and animal cells share common components such as the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, and mitochondria. However, there are some differences between both the cells which are discussed below:
- Size: Usually, animal cells are smaller in size than plant cells. Moreover, plant cells have a fixed rectangular shape, whereas animal cells have a round or irregular shape.
- Cell wall: Cell wall is present in a plant cell, but absent in an animal cell. The main purpose of the cell wall in a plant cell is to provide support and give shape to the plants.
- Location of the cell membrane: Both animal and plant cells have a cell membrane, however, the cell membrane in the plant cell is located between the cell wall and the cytoplasm. On the other hand, the cell membrane in an animal cell is present on the external surface of the cell. In an animal cell, it is a border that segregates the interior of the cell from the external environment.
- Chloroplasts: Plant cells have chloroplasts whereas animal cells do not. Through chloroplasts, plants can make their own food through a process known as photosynthesis.
- Vacuole: Generally, plant cells have one or more large vacuole(s). On the other hand, animal cells have smaller vacuoles, if they are present. Large vacuoles in plant cells give them shape and enable them to store food and water for future use. The vacuoles in the animal cells are smaller because the storage function plays a lesser role in these cells as compared to the plant cells.
- Nucleus: Both plant and animal cells contain a nucleus that stores genetic information. The location of the nucleus in both cells is different. In animal cells, the nucleus is present in the central region of the cell, whereas, in the plant cell, the nucleus is present more on the periphery because a large water-filled vacuole is located in the centre of the cell.
The following table summarizes the differences between a plant and an animal cell.
| Plant Cells | Animal Cells |
|---|---|
| Are large and have a rectangular shape | Are small and have a round of irregular shape |
| They have cell wall | They do not have cell wall |
| The nucleus is present on one side of the cell | The nucleus is present in the center of the cell |
| Contain one large vacuole | Contain many smaller vacuoles |
| Have chloroplasts | Do not have chloroplasts |













Very interesting and nice
I learned a lot from this
I love it it really helps me